In this article Stack using linked list we give the information about stack can be implemented using linked list. This is known as dynamic implementation of stack.
Stack using linked list:
Stack can be implemented using linked list. This is known as dynamic implementation of stack. Using linked list-
- Stack can grow to any size.
- When an element is popped (Remove), the memory can be freed.
- In stack only, the topmost element can be accessed; the first node in the stack can be accessed by a pointer called top.
- Every element pushed will be added to the beginning of the linked list.
struct node
{
int info;
struct node *next;
};
typedef struct node NODE;
NODE *top;
The push and pop operations of stack are as shown below:
- Initially, Stack is Empty
Top=NULL;
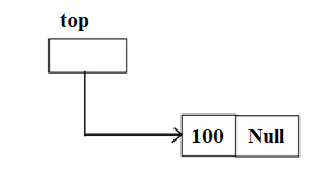
- Push 10
- Push 20
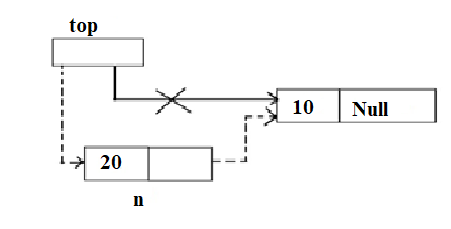
n->next=top;
top=n;
- Pop
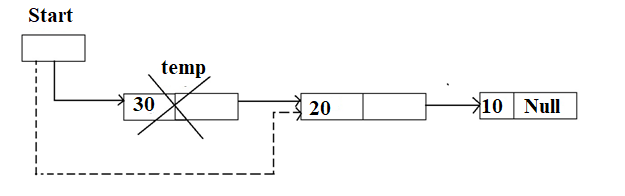
Temp=top;
Top=top->next;
Free(temp);
Program:
/* program of stack using linked list */
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
struct node
{
int info;
struct NODE *next;
};
typedef struct node NODE;
node *top=NULL;
void main()
{
int ch;
void push();
void pop();
void display();
while(1)
{
clrscr();
printf(“\n 1. Push”);
printf(“\n 2. Pop”);
printf(“\n 3. Display”);
printf(“\n 4. Quit”);
printf(“\n Enter your choice: ”);
scanf(“%d”,&ch);
switch(ch)
{
case 1:
push();
break;
case 2:
pop();
break;
case 3:
display();
break;
case 4:
exit(0);
default:
printf(“\n Enter correct choice…”);
}
}
}
void push()
{
NODE *n;
int data;
n=(NODE*)malloc(sizeof(NODE));
printf(“\n Enter data to push: ”);
scanf(“%d”,&data);
n->info=data;
n->next=top;
top=n;
getch();
}
void pop()
{
NODE *temp;
if(top==NULL)
{
printf(“\n Stack is empty…”);
}
else
{
temp=top;
printf(“\n Popped element is %d”,temp->info);
top=top->next;
free(temp);
}
getch();
}
void display()
{
NODE *temp;
temp=top;
if(top==NULL)
printf(“\n Stack is empty…”);
else
{
printf(“\n Stack elements are: ”);
while(temp!=NULL)
{
printf(“%d\n”,temp->info);
temp=temp->next;
}
}
getch();
}
Some More:
POP- Introduction to Programming Using ‘C’
OOP – Object Oriented Programming
DBMS – Database Management System
RDBMS – Relational Database Management System
Join Now: Data Warehousing and Data Mining