In this article type of inheritance we give the information about type of inheritance in C++ such as single, multiple, multilevel, Hierarchical and hybrid inheritance.
Type of inheritance in C++:-
There are 5 types of inheritance found in C++.
- Single inheritance
- Multiple inheritance
- Multilevel inheritance
- Hierarchical inheritance
- Hybrid inheritance
Single Inheritance:-
In this type of inheritance we take two classes in which the property of the base class is inherited in a derive class.
Definition:
“A derived class with only one base class is known as single inheritance.”
Single Inheritance
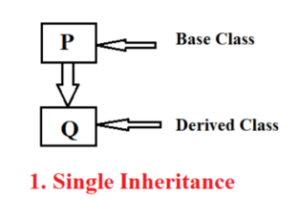
A class Q can inherit the attributes of class P as shown in figure above is knows as Single inheritance.
Its syntax is given below –
Syntax:
class Q : visibility P
{
Member of Q class;
Access P class member;
}
Source Code:
// Single Inheritance in C++
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class P // Base class
{
private:
int a; // data member
public:
int b; // data member
void getab() // member function
{
cout<<“\n Enter the 2 numbers: “;
cin>>a>>b;
}
int geta()
{
return a;
}
};
class Q: public P // Derived Class
{
private:
int c; // data member
public:
void mul()
{
c = b * geta(); // access value of a using geta function
}
void display()
{
cout<<“\n A*B = “<<c;
}
};
void main()
{
Q obj; // create derived class object
clrscr();
obj.getab();
obj.geta();
obj.mul();
obj.display();
getch();
}
OUTPUT:-
Enter the 2 numbers: 15
2
A*B = 30
Multiple Inheritance:
Definition:
“A derived class with several base classes is called multiple inheritance.”
Multiple Inheritance

A class R can inherit the attributes of classes P and Q as shown in figure above is knows as multiple inheritance.
The syntax of a derived class with multiple base classes is as follows:
class R : visibility P, visibility Q
{
Member of R class;
Access P and Q class member;
}
Source Code:
// Multiple Inheritance
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class M // 1st Base Class
{
protected:
int x; // data member
public:
void getx() // member function
{
cout<<“\n\n Enter the number 1st number : “;
cin>>x;
}
};
class N // 2nd base class
{
protected:
int y; // data member
public:
void gety() // member function
{
cout<<“\n Enter the number 2nd number: “;
cin>>y;
}
};
class P: public M, public N // derived class
{
public:
void mul(); // member function
};
void P::mul()
{
cout<<“\n Value of X: ” <<x;
cout<<“\n Value of Y: ” <<y;
cout<<“\n X*Y = “<<x*y;
}
void main()
{
P obj;
clrscr();
obj.getx();
obj.gety();
obj.mul();
getch();
}
OUTPUT:
Enter the number 1st number:
10
Enter the number 2nd number:
20
Value of X: 10
Value of Y: 20
X*Y = 200
Some More:
POP- Introduction to Programming Using ‘C’
OOP – Object Oriented Programming
DBMS – Database Management System
RDBMS – Relational Database Management System
Join Now: Data Warehousing and Data Mining