In this article Multilevel Inheritance we give the information about The mechanism of deriving a class from another derived class is known as multilevel inheritance.
Multilevel inheritance:-
Definition:
“The mechanism of deriving a class from another derived class is known as multilevel inheritance.”
Multilevel Inheritance

A derived class R can inherit the attributes of another derived class Q as shown in figure above is knows as multilevel inheritance.
Above figure class P serves as a base class for derived class Q, which in turn serves as a base class for derived class R. The class Q is known as intermediate base class since it provides a link for the inheritance between P and R. The chain PQR is known as inheritance path.
A derived class with multilevel inheritance is declared as follows:-
class P {…….}; // base calss
class Q : public P {……….}; // Q derived from P
class R : public Q {……….}; // R derived from Q
// Multilevel Inheritance Program
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class stud // base class
{
protected:
int roll_no; // data member
public:
void getnum() // member function
{
cout<<“\n Enter the Roll Number: “;
cin>>roll_no;
}
};
class test:public stud // 1st derived class
{
protected:
int c,cpp,java; // data member
public:
void getmarks() // member function
{
cout<<“\n Enter the 3 subject marks: “;
cin>>c>>cpp>>java;
}
};
class result: public test // 2nd derived class
{
int tot; // data member
public:
void display(); // member function
};
void result::display()
{
tot=c+cpp+java;
cout<<“\n\n Roll Number: “<<roll_no;
cout<<“\n C Programming: “<<c;
cout<<“\n CPP Programming: “<<cpp;
cout<<“\n Java Programming: “<<java;
cout<<“\n Total: “<<tot;
}
void main()
{
result p;
clrscr();
p.getnum();
p.getmarks();
p.display();
getch();
}
OUPUT:
Enter the Roll Number:
1
Enter the 3 subject marks:
80
70
90
Roll Number: 1
C Programming: 80
CPP Programming: 70
Java Programming: 90
Total: 240
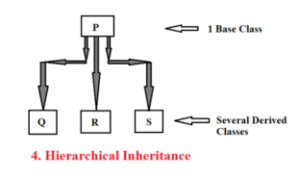
Hierarchical inheritance in C++:
Definition:
“Several derived classes with only one base class is known as Hierarchical inheritance.”
For example, C, C++, Java are derived from Programming class. Similarly, Apple, Orange, Banana are derived from Fruits class.
Hierarchical Inheritance
Syntax of Hierarchical Inheritance
class base_class
{
… .. …
};
class first_derived_class: public base_class
{
… .. …
};
class second_derived_class: public base_class
{
… .. …
};
class third_derived_class: public base_class
{
… .. …
};
……..
……..
……..
Source Code:
//Hierarchical Inheritance
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class data // Base Class
{
protected:
int x,y; // data members
public:
void getxy() // member function
{
cout<<“\n Enter the 2 numbers: “;
cin>>x>>y;
}
};
class derived1: public data // 1st derived class
{
public:
void maxnum()
{
if(x>y)
cout<<“\n 1st number is largest : “<<x;
else
cout<<“\n 2nd number is largest : “<<y;
}
};
class derived2: public data
{
public:
void swap()
{
int t=0;
cout<<“\n Before swap X: “<<x<<“\t Y: “<<y;
t=x;
x=y;
y=t;
cout<<“\n After swap X: “<<x<<“\t Y:”<<y;
}
};
void main()
{
derived1 p; // create object for 1st derived class
clrscr();
p.getxy();
p.maxnum();
derived2 q; // create object for 2nd derived class
q.getxy();
q.swap();
getch();
}
OUTPUT:
Enter the 2 numbers: 100
50
1st number is largest : 100
Enter the 2 numbers: 7
9
Before swap X: 7 Y: 9
After swap X: 9 Y: 7
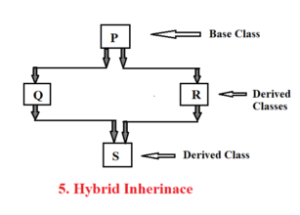
Hybrid Inheritance:
Hybrid inheritance is a collection of multiple and multi-level inheritance. It has more than one base class and more than one derive class-
Hybrid Inheritance
Syntax for Hybrid Inheritance (Multilevel, Multiple)
class base_class_N
{
//body_of_Base_class
};
class derived_class_N1 : Access_Specifier base_class_Name
{
//body_of_derived_class1
};
class derived_class_N2
{
//body_of_derived_class2
};
class derived_class_N3 : class derived_class_N1, class derived_class_N2
{
//body_of_derived_class3
};
Source Code:-
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class first
{
protected:
int a,b;
public:
void get_num(int x, int y)
{
a = x;
b = y;
}
}; // first class terminate
class second:public first
{
protected:
int sum;
public:
void get_sum()
{
sum = a+b; // access first class data-member
}
}; //second class terminate
class third
{
protected:
int m,n, mul;
public:
void get(int x,int y)
{
m = x; // access second class member
n = y; // access second class member
mul = m*n;
}
}; // third class terminate
class fourth:public second,public third
{
public:
void show_all()
{
cout<<“\nTotal: “<<a<<“+”<<b<<” = “<<sum;
cout<<“\nMultiplicatoin: “<<m<<“x”<<n<<” = “<<mul;
}
}; //fourth class terminate
void main()
{
int a,b;
clrscr();
fourth obj; // fourth class object declare
cout<<“Enter two number: “;
cin>>a>>b;
obj.get_num(a,b); // class first member
obj.get(a,b); // class second member call
obj.get_sum(); // class second member call
obj.show_all(); // class fourth member call
getch();
}
OUTPUT:-
Enter two number: 4
7
Total: 4+7 = 11
Multiplication: 4×7 = 28
Some More:
POP- Introduction to Programming Using ‘C’
OOP – Object Oriented Programming
DBMS – Database Management System
RDBMS – Relational Database Management System
Join Now: Data Warehousing and Data Mining