In this article AWT in Java we give the information about it is a platform dependent API that creates a graphical user interface (GUI) for Java programs.
AWT in Java (Abstract Window Toolkit)
Introduction
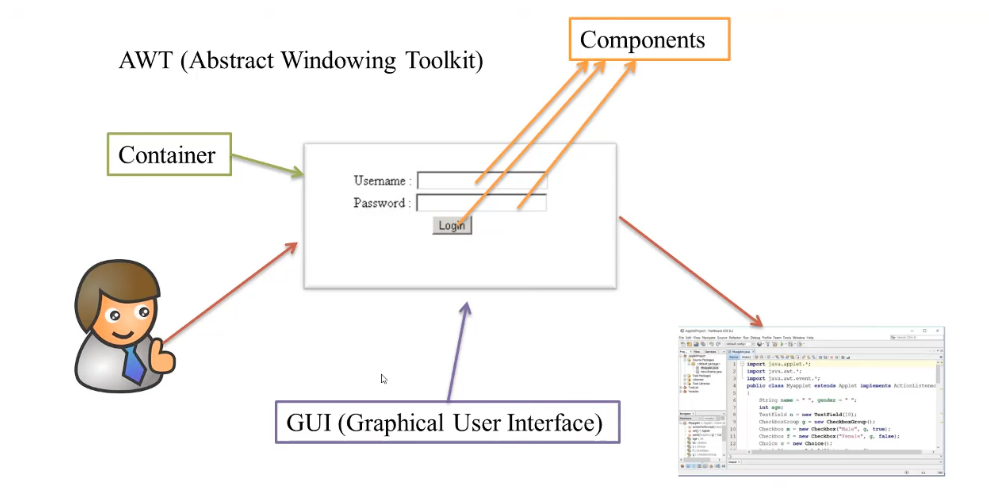
AWT (Abstract Window Toolkit) is a Java API used to create Graphical User Interface (GUI) or Windows-based applications.
In simple terms:
“Java AWT is an API through which GUI or window-based applications are developed in Java.”
It provides a set of classes and interfaces to create GUI components like Button, Label, TextField, Checkbox, Menu, etc.
Java AWT hierarchy:-
Java AWT classes are shown below:-

Components:- All elements like buttons, text fields, scrollbars etc. are components.
Container:- Container is a component of AWT which contains other components such as buttons, textfield, checkbox, label etc. and it also controls the layout of the components.
Container is a subclass of component class.
Window:- Window is a container which has no border and menu bar. To create a window we have to use frame and dialog or other windows.
Panel:- Panel does not contain title bar, menu bar or border. It is used to contain components. Like:- button, textfield etc.
Frame:- Frame is a container that contains the title bar, menu bar or border. It also contains other components like:- buttons, textfields, scrollbars etc. This container is most used in developing applications in java AWT.
Key Points of AWT
- AWT is platform-dependent:
The components depend on the native operating system.
Example: a button may look different on Windows, macOS, or Linux. - AWT is heavyweight:
AWT components use native OS resources (peer components). - AWT is part of the java.awt package.
- AWT is the foundation of Swing:
Swing components are built on top of AWT but are lightweight and platform-independent.
Basic Terms
| Term | Description |
| Component | All visual GUI elements like buttons, text fields, scrollbars, etc. |
| Container | A special component that can hold other components (e.g., Frame, Panel). |
| Panel | A simple container that holds GUI elements; it has no title bar or border. |
| Window | A top-level container without a title bar or menu. |
| Frame | A top-level container with a title bar, menu bar, and border. |
| Dialog | A pop-up window used for short messages or input. |
Common AWT Methods
| Method | Description |
| add(Component c) | Adds a component to the container. |
| setSize(int width, int height) | Sets the width and height of the window or component. |
| setLayout(LayoutManager m) | Sets the layout manager for arranging components. |
| setVisible(boolean b) | Sets the visibility of the component (true = visible). |
Example: Simple AWT Program
// Importing Java AWT package
import java.awt.*;
// Extending Frame class
public class AWTExample1 extends Frame {
// Constructor
AWTExample1() {
// Create a button
Button b = new Button(“Click Me!!”);
// Set button position and size
b.setBounds(30, 100, 80, 30);
// Add button to frame
add(b);
// Set frame size
setSize(300, 300);
// Set frame title
setTitle(“This is our basic AWT example”);
// No layout manager (absolute positioning)
setLayout(null);
// Make frame visible
setVisible(true);
}
// Main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create instance of AWTExample1
new AWTExample1();
}
}
Output:
A window titled “This is our basic AWT example” appears with a “Click Me!!” button.
Key Characteristics of AWT Components
| Property | Description |
| Platform-dependent | Look and feel depends on the OS. |
| Heavyweight | Uses native system resources. |
| Limited UI controls | Basic components only (e.g., Button, Label). |
| Less flexible | Cannot easily customize appearance. |
| Foundation for Swing | Swing builds upon AWT and overcomes its limitations. |
Summary
- AWT is the original Java GUI toolkit.
- It is heavyweight and platform-dependent.
- Uses native system components for rendering.
- Swing is preferred for new applications because it is lightweight, faster, and fully customizable.
Some More:
POP- Introduction to Programming Using ‘C’
OOP – Object Oriented Programming
DBMS – Database Management System
RDBMS – Relational Database Management System
Join Now: Data Warehousing and Data Mining