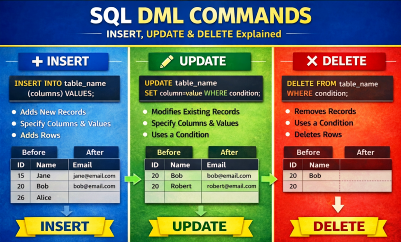
Learn SQL DML commands INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE with syntax, rules, and examples. Understand how to add, modify, and delete records in database tables.
SQL DML Commands
What is Insert?
INSERT is a DML (Data Manipulation Language) command used to add new records (rows) into a table.
Basic Syntax of INSERT
1) Insert values into all columns (same order as table)
INSERT INTO table_name
VALUES (value1, value2, value3, …);
Rules
- Number of values must match number of columns
- Order of values must be same as table columns
- Data types must match
Example
INSERT INTO Supplier
VALUES (101, ‘Vandana’, ‘Goa’, ‘9876543210’);
2) Insert values into specific columns
Recommended method (safer)
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, column3)
VALUES (value1, value2, value3);
Example
INSERT INTO Supplier (SId, SName, City)
VALUES (102, ‘Rohan’, ‘Pune’);
Remaining columns will take:
- DEFAULT value or
- NULL (if allowed)
3) Insert multiple rows at once
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, column3)
VALUES
(value1, value2, value3),
(value4, value5, value6),
(value7, value8, value9);
Example
INSERT INTO Supplier (SId, SName, City)
VALUES
(103, ‘Anita’, ‘Mumbai’),
(104, ‘Suresh’, ‘Delhi’),
(105, ‘Meena’, ‘Chennai’);
4) Insert records from another table (INSERT…SELECT)
INSERT INTO table_name1 (column1, column2)
SELECT columnA, columnB
FROM table_name2
WHERE condition;
Example
INSERT INTO Old_Supplier (SId, SName)
SELECT SId, SName
FROM Supplier
WHERE City = ‘Delhi’;
5) Insert DEFAULT values
INSERT INTO table_name DEFAULT VALUES;
(works when table has default column definitions)
6) Insert with NULL values
INSERT INTO Supplier (SId, SName, City)
VALUES (106, ‘Rita’, NULL);
What is UPDATE?
UPDATE is a DML (Data Manipulation Language) command used to:
- modify existing records (rows)
- change one or more column values
- update single or multiple rows
Basic Syntax of UPDATE
Update one or more columns with a condition
UPDATE table_name
SET column1 = value1,
column2 = value2
WHERE condition;
Important: Always use WHERE unless you want to change all rows.
Example 1 — Update single column
Change city of supplier Vandana to Goa
UPDATE Supplier
SET City = ‘Goa’
WHERE SName = ‘Vandana’;
Example 2 — Update multiple columns
UPDATE Supplier
SET City = ‘Mumbai’,
Phone = ‘9999999999’
WHERE SId = 101;
Example 3 — Update ALL rows (no WHERE)
UPDATE Supplier
SET City = ‘BOMBAY’;
This changes city of every supplier.
Example 4 — Conditional update using operators
Update salary where salary is less than 20000
UPDATE Employee
SET Salary = 20000
WHERE Salary < 20000;
Example 5 — Update using pattern (LIKE)
Update city where name starts with A
UPDATE Supplier
SET City = ‘Delhi’
WHERE City LIKE ‘A%’;
Example 6 — Update using subquery
UPDATE Employee
SET Department = ‘IT’
WHERE DeptNo = (
SELECT DeptNo FROM Department WHERE DeptName = ‘Information Tech’
);
Example 7 — Update with NULL
UPDATE Student
SET Email = NULL
WHERE RollNo = 5;
SQL DML Commands
What is DELETE?
DELETE is a DML (Data Manipulation Language) command used to:
- remove records (rows) from a table
- delete selected rows using a condition
- delete all rows (if no condition)
It does not delete the table structure.
Basic Syntax of DELETE
Delete rows with a condition
DELETE FROM table_name
WHERE condition;
Only the rows matching the condition will be deleted.
Important Rule
- Always use WHERE unless you want to delete all rows
- Without WHERE → entire table becomes empty
Example 1 — Delete one record
Delete supplier whose SID = 204001
DELETE FROM Supplier
WHERE SID = 204001;
Example 2 — Delete records matching text condition
Delete students who live in Pune
DELETE FROM Student
WHERE City = ‘Pune’;
Example 3 — Delete records using pattern (LIKE)
Delete suppliers whose city starts with A
DELETE FROM Supplier
WHERE City LIKE ‘A%’;
Example 4 — Delete all rows from a table
DELETE FROM Supplier;
Table becomes empty
Structure remains
Use carefully
Example 5 — Delete using multiple conditions
DELETE FROM Employee
WHERE Department = ‘HR’ AND Salary < 20000;
Example 6 — Delete using subquery
Delete records from Supplies for suppliers in Delhi
DELETE FROM Supplies
WHERE SID IN (
SELECT SID FROM Supplier WHERE City = ‘Delhi’
);
About FOREIGN KEY Error (Very Important for Exams)
If you try to delete a parent row with child records, MySQL may show:
Cannot delete or update a parent row: a foreign key constraint fails
Solution:
- delete child table rows first
- then delete parent table rows
Example:
DELETE FROM Supplies
WHERE SID = 204001;
DELETE FROM Supplier
WHERE SID = 204001;
Difference between DELETE, TRUNCATE, DROP
| Command | What it does | Undo possible |
| DELETE | Deletes rows | Yes |
| TRUNCATE | Removes all rows (fast) | No |
| DROP | Deletes entire table | No |
SQL DML Commands
DML Commands Examples
- Insert at least 10 records in tables Supplier, Part, and Supplies
Supplier Table:
INSERT INTO SUPPLIER VALUES
(204001, ‘Vandana’, ‘Electronics’, 9876543110, ‘Delhi’, ‘Delhi’),
(204002, ‘Ramesh’, ‘Mechanical’, 9811122233, ‘Mumbai’, ‘Mumbai’),
(204003, ‘Sanjay’, ‘Hardware’, 9822334455, ‘Pune’, ‘Pune’),
(204004, ‘Kavita’, ‘Automobile’, 9898989898, ‘Delhi’, ‘Delhi’),
(204005, ‘Vikas’, ‘Electrical’, 9977665544, ‘Ahmedabad’, ‘Ahmedabad’),
(204006, ‘Anita’, ‘Computer’, 9900112233, ‘Chennai’, ‘Chennai’),
(204007, ‘Meena’, ‘Civil’, 9123456780, ‘Delhi’, ‘Delhi’),
(204008, ‘Rahul’, ‘Textile’, 9234567812, ‘Kolkata’, ‘Kolkata’),
(204009, ‘Vaishali’, ‘Chemical’, 9345678921, ‘Goa’, ‘Goa’),
(204010, ‘Alka’, ‘Production’, 9456789032, ‘Agra’, ‘Agra’);
Part Table:
INSERT INTO PART (PID, PNAME, COLOR, PRICE) VALUES
(301, ‘Bolt’, ‘Red’, 5),
(302, ‘Nut’, ‘Blue’, 3),
(303, ‘Screw’, ‘Black’, 2),
(304, ‘Washer’, ‘Red’, 1),
(305, ‘Gear’, ‘Silver’, 50),
(306, ‘Bearing’, ‘Grey’, 80),
(307, ‘Wheel’, ‘Black’, 120),
(308, ‘Rod’, ‘Blue’, 40),
(309, ‘Pipe’, ‘Green’, 70),
(310, ‘Plate’, ‘Red’, 30);
Supplies Table:
INSERT INTO SUPPLIES (SID, PID, qty, date_supplied) VALUES
(204001, 301, 200, ‘2025-01-05’),
(204001, 302, 150, ‘2025-01-08’),
(204002, 305, 50, ‘2025-01-10’),
(204003, 306, 75, ‘2025-01-12’),
(204004, 303, 180, ‘2025-01-14’),
(204005, 307, 25, ‘2025-01-16’),
(204006, 304, 400, ‘2025-01-18’),
(204007, 308, 120, ‘2025-01-20’),
(204008, 309, 90, ‘2025-01-22’),
(204009, 310, 60, ‘2025-01-24’),
(204010, 301, 140, ‘2025-01-26’),
(204003, 305, 30, ‘2025-01-28’);
- Show the contents in tables Supplier, Part, and Supplies
Supplier Table:
SELECT * FROM Supplier;
Part Table:
SELECT * FROM Part;
Supplies Table:
SELECT * FROM Supplies;
- Find the name and State of all suppliers
MySQL> SELECT SName, State FROM Supplier;
- Find the name and phone number of all suppliers who stay in ‘Delhi’
SELECT SName, PhoneNo
FROM Supplier
WHERE State = ‘Delhi’;
-
Find all distinct branches of suppliers
SELECT DISTINCT branch
FROM Supplier;
- Delete the record of the supplier whose SID is 204001
Note: You cannot delete a supplier if it is referenced in Supplies.
Solution: Delete child rows first.
DELETE FROM Supplies WHERE SID = 204001;
DELETE FROM Supplier WHERE SID = 204001;
- Delete all records of the Supplier table
MDELETE FROM Supplier;
- Delete all records of suppliers whose city starts with capital ‘A’
DELETE FROM Supplies
WHERE SID IN (SELECT SID FROM Supplier WHERE city LIKE ‘A%’);
DELETE FROM Supplier
WHERE city LIKE ‘A%’;
- Find the supplier names which have ‘lk’ in any position
SELECT SName
FROM Supplier
WHERE SName LIKE ‘%lk%’;
- Find the supplier names where ‘a’ is in the second position
SELECT *
FROM Supplier
WHERE SName LIKE ‘_a%’;
- Find the name of suppliers whose name starts with ‘V’ and ends with ‘A’
SELECT SName
FROM Supplier
WHERE SName LIKE ‘V%A’;
- Change the city of all suppliers to ‘BOMBAY’
UPDATE Supplier
SET city = ‘BOMBAY’;
- Change the city of supplier ‘Vandana’ to ‘Goa’
UPDATE Supplier
SET city = ‘Goa’
WHERE SName = ‘Vandana’;
- POP- Introduction to Programming Using ‘C’
- DS – Data structure Using C
- OOP – Object Oriented Programming
- Java Programming
- DBMS – Database Management System
- RDBMS – Relational Database Management System
- https://defineinfoloop.blogspot.com/?m=1