In this article SQL DDL Commands we Learn SQL DDL commands DESC and TRUNCATE with clear syntax, examples, differences, and exam-oriented explanations. Ideal for BCA, DBMS, and beginners.
SQL DDL Commands
SQL(Structured Query Language) Components:
SQL consists of several components. One of the most important components is DDL (Data Definition Language).
DDL – Data Definition Language: DDL commands are used to define and manage database structures, such as databases, tables, views, and schemas.
DDL Commands: It includes the following five commands:
- CREATE
- ALTER
- DESC (DESCRIBE)
- DROP
- TRUNCATE
1. CREATE Command
The CREATE command is used to create database objects such as:
- Database
- Table
- View
- Sequence
- Function
- Procedure
- Trigger
Create a New Database
Syntax:
CREATE DATABASE database_name;
Example:
CREATE DATABASE bca;
Show Databases
The SHOW DATABASES command displays the list of existing databases.
Syntax:
SHOW DATABASES;
Output:
Databases
information_schema
mysql
test
Select a Database
The USE command is used to select a particular database.
Syntax:
USE database_name;
Example:
USE bca;
(Database changed)
Show Tables
Displays all tables in the selected database.
Syntax:
SHOW TABLES;
CREATE TABLE Command
The CREATE TABLE command is used to create a new table in a database.
The user must specify:
- Table name
- Column names
- Data types
- Constraints
Syntax
CREATE TABLE table_name (
column1 datatype(size),
column2 datatype(size),
column3 datatype(size),
… );
Example: Student Table
Create a table to store student information:
CREATE TABLE std_info (
rollno INT(2) PRIMARY KEY,
sname VARCHAR(15),
address VARCHAR(30)
);
Output:
Query OK.
Check the table:
SHOW TABLES;
Output:
Tables_in_bca
std_info
Example Schema
Consider the following schema:
- Supplier (SID, sname, branch, city, phone)
- Part (PID, pname, color, price)
- Supplies (SID, PID, qty, date_supplied)
-
Supplier Table
Datatypes and Sizes
| Attribute | Data Type | Size |
| SID | VARCHAR | 5 |
| sname | VARCHAR | 20 |
| branch | VARCHAR | 20 |
| city | VARCHAR | 25 |
| phoneNO | VARCHAR | 13 |
SQL Command:
CREATE TABLE supplier (
SID VARCHAR(5) PRIMARY KEY,
sname VARCHAR(20),
branch VARCHAR(20),
city VARCHAR(25),
phoneNO VARCHAR(13)
);
-
Part Table
Datatypes and Sizes
| Attribute | Data Type | Size | Description |
| PID | VARCHAR | 5 | Unique ID |
| pname | VARCHAR | 20 | Part name |
| color | VARCHAR | 20 | Color |
| price | DECIMAL | (10,2) | Monetary value |
SQL Command:
CREATE TABLE part (
PID VARCHAR(5) PRIMARY KEY,
pname VARCHAR(20),
color VARCHAR(20),
price DECIMAL(10,2) NOT NULL
);
-
Supplies Table
Datatypes, Sizes, and Constraints
| Attribute | Data Type | Size | Description |
| SID | VARCHAR | 5 | References supplier |
| PID | VARCHAR | 5 | References part |
| qty | INT | 7 | Quantity supplied |
| date_supplied | DATE | — | Supply date |
SQL Command:
CREATE TABLE supplies (
SID VARCHAR(5),
PID VARCHAR(5),
qty INT(7) NOT NULL,
date_supplied DATE,
PRIMARY KEY (SID, PID, date_supplied),
FOREIGN KEY (SID) REFERENCES supplier(SID),
FOREIGN KEY (PID) REFERENCES part(PID)
);
2. ALTER Command
The ALTER command is used to modify the structure of an existing table.
ALTER Sub-Commands
- ADD
- DROP COLUMN
- MODIFY
- RENAME
I. ADD Column
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD column_name datatype(size);
Example:
Q.1 Add a new column state to the supplier table.
ALTER TABLE supplier ADD state VARCHAR(15);
II. DROP COLUMN
Used to remove a column from a table.
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE table_name DROP COLUMN column_name;
Example:
Q. 2 Remove attribute city from supplier table
ALTER TABLE supplier DROP COLUMN city;
III. MODIFY Column
Used to change data type, size, constraints, or nullability.
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE table_name MODIFY column_name datatype(size);
Example:
Q. 3 Modify the data type of phone attribute
ALTER TABLE supplier MODIFY phoneNO INT(13);
IV. CHANGE Column Name
Used to rename a column.
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE table_name CHANGE old_column new_column datatype(size);
Example:
Q. 5 Change the name of attribute city to address
ALTER TABLE supplier CHANGE city address VARCHAR(50);
V. RENAME Table
Used to rename an existing table.
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE table_name RENAME TO new_table_name;
Example:
Q. 6 Change a table’s name, supplier to sup
ALTER TABLE supplier RENAME TO sup;
3. DROP Command
The DROP command permanently removes a table along with its structure from the database.
Syntax:
DROP TABLE table_name;
Example:
Q. 7 Remove the part table from database
DROP TABLE student;
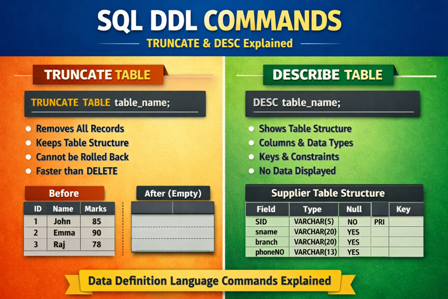
4. DESC (DESCRIBE) Command
The DESC command is used to display the structure of a table.
It shows information about table columns such as:
- Column name
- Data type
- Size
- Null / Not Null constraint
- Key (Primary / Foreign key)
- Default value
- Extra information
DESC does not display table data, only the table structure.
Syntax
DESC table_name;
or
DESCRIBE table_name;
(Both commands work the same)
Example
Consider the table supplier.
DESC supplier;
Sample Output
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
| SID | varchar(5) | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| sname | varchar(20) | YES | NULL | ||
| branch | varchar(20) | YES | NULL | ||
| phoneNO | varchar(13) | YES | NULL |
Uses of DESC Command
- To verify table structure
- To check column names and data types
- To know primary key and constraints
- Helpful before writing INSERT or SELECT queries
Important Points
- DESC is a DDL-related utility command
- Used only for viewing table structure
- Does not modify the table
- Works in MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL (as DESCRIBE)
5. TRUNCATE Command in SQL
TRUNCATE Command
The TRUNCATE command is a DDL (Data Definition Language) command used to remove all records from a table very quickly.
TRUNCATE deletes all rows but keeps the table structure intact.
Syntax
TRUNCATE TABLE table_name;
Example
TRUNCATE TABLE student;
Result:
- All records from the student table are removed
- Table structure (columns, constraints) remains unchanged
- Table becomes empty
Features of TRUNCATE Command
- Removes all rows from a table
- Faster than DELETE
- Cannot use WHERE clause
- Resets AUTO_INCREMENT value
- Does not fire triggers
- Cannot be rolled back in most databases
Key Highlights
DDL commands affect database structure
- CREATE is used to create database objects
- ALTER modifies existing tables
- DROP deletes table structure permanently
- TRUNCATE removes all records but keeps table structure
- Primary Key ensures uniqueness
- Foreign Key maintains referential integrity
- POP- Introduction to Programming Using ‘C’
- DS – Data structure Using C
- OOP – Object Oriented Programming
- Java Programming
- DBMS – Database Management System
- RDBMS – Relational Database Management System
- https://defineinfoloop.blogspot.com/?m=1