Strassen Matrix Multiplication uses Divide & Conquer to multiply large matrices efficiently. Learn the algorithm, steps, time complexity, advantages, and applications.
Strassen Matrix Multiplication
(Strassen’s Matrix Multiplication Method)
Introduction
Strassen’s Matrix Multiplication Algorithm is an advanced and efficient Divide and Conquer–based algorithm used to multiply two square matrices faster than the traditional method.
In the traditional matrix multiplication algorithm, the time complexity is O(n³).
Strassen reduced this complexity to:
O(nlog27)≈O(n2.81)
which makes it significantly faster for large matrices.
Need for Strassen’s Algorithm
When the size of matrices becomes large, the traditional matrix multiplication method becomes very time-consuming.
Strassen’s algorithm:
- Reduces the number of multiplications
- Is more efficient for large matrices
- Improves overall performance in matrix computations
Divide and Conquer Approach
Strassen’s algorithm is based on the Divide and Conquer technique.
Divide Step
Let A and B be two square matrices of size n × n.
Each matrix is divided into four equal sub-matrices:
Matrix A:
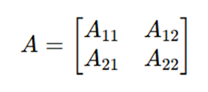
Matrix B:
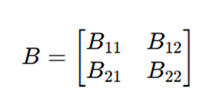
Traditional Method vs Strassen Method
Traditional Matrix Multiplication
- Requires 8 multiplications
- Requires 4 additions
- Time Complexity: O(n³)
Strassen’s Method
- Requires only 7 multiplications
- Uses some extra additions and subtractions
- Time Complexity: O(n^{\log_2 7}) ≈ O(n^{2.81})
Strassen’s Seven Multiplications
Strassen proposed the following seven intermediate products:
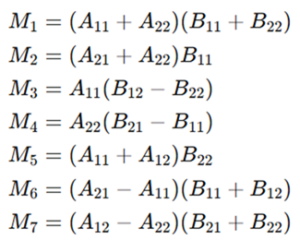
Final Result Matrix (Combine Step)
Using the above intermediate values, the result matrix C is obtained as:
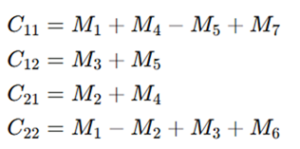
Algorithm Steps
- If the matrix size is 1 × 1, multiply directly (Base Case)
- Divide each matrix into four sub-matrices
- Perform 7 recursive multiplications
- Combine the sub-results to form the final result matrix
Time Complexity Analysis
The recurrence relation for Strassen’s algorithm is:
T(n)=7T(n/2)+O(n2)
Using Master’s Theorem, we get:
T(n)=O(nlog27)≈O(n2.81)
This is asymptotically better than the traditional O(n³) algorithm.
Advantages
- Reduces the number of multiplications
- Faster for large matrices
- Efficient use of the Divide and Conquer technique
- Useful in high-performance and scientific computing
Disadvantages
- Not efficient for small matrices
- Requires extra additions and more memory
- Implementation is complex
- May suffer from numerical stability issues
Applications
- Scientific computing
- Computer graphics
- Image processing
- Machine learning and Artificial Intelligence
- High-performance computing systems
Conclusion
Strassen’s Matrix Multiplication Algorithm is a powerful Divide and Conquer–based technique that significantly speeds up matrix multiplication.
Although it is not suitable for small matrices, it outperforms the traditional method for large matrices and is widely used in advanced computing applications.
See More:
- POP- Introduction to Programming Using ‘C’
- DS – Data structure Using C
- OOP – Object Oriented Programming
- Java Programming
- DBMS – Database Management System
- RDBMS – Relational Database Management System
- https://defineinfoloop.blogspot.com/?m=1