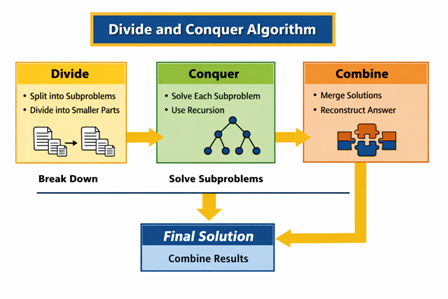
In this article Divide and Conquer is an algorithm design technique that breaks a problem into smaller parts, solves them recursively, and combines the solutions.
Divide and Conquer Algorithm:
1. Basic Concept of Divide and Conquer
Divide and Conquer is an important algorithm design technique. In this method, you break a large and complex problem into smaller subproblems, solve each subproblem, and then combine the results to get the final answer.
In simple terms:
Break → Solve → Combine → Final Answer
2. Three Main Stages of Divide and Conquer
1. Divide
- You divide the given problem into several smaller subproblems.
- Each subproblem remains similar to the original problem but becomes smaller in size.
2. Conquer
- You solve each subproblem independently.
- If a subproblem becomes very small, you solve it directly (Base Case).
- Otherwise, you apply Divide and Conquer again using recursion.
3. Combine
- You combine the solutions of all subproblems to get the final solution.
3. General Structure of Divide and Conquer
DivideAndConquer(problem)
{
if (problem is small enough)
solve directly;
else
{
divide the problem into subproblems;
solve each subproblem recursively;
combine the solutions;
}
}
4. Importance of the Base Case
- The base case defines a situation where you can solve the problem directly.
- Without a base case, recursion continues forever and leads to infinite looping.
- Therefore, the base case plays a crucial role in Divide and Conquer.
5. Advantages of Divide and Conquer
- You can solve large problems more easily.
- The algorithm becomes clearer and more modular.
- You often get faster and more efficient solutions.
- Recursion simplifies the code and improves readability.
- You can use this method in parallel processing.
6. Disadvantages of Divide and Conquer
- Recursive programs use more stack memory.
- Some problems require complex and time-consuming combine steps.
- The method does not fit every type of problem.
7. Examples of Algorithms Using Divide and Conquer
- Binary Search – you repeatedly divide the array into two halves.
- Merge Sort – you divide the array, sort each part, and merge them.
- Quick Sort – you choose a pivot and partition the array.
- Strassen’s Matrix Multiplication – you divide matrices into submatrices.
- Tower of Hanoi – you break the problem into smaller disk movements.
8. Relationship Between Divide and Conquer and Recursion
- Programmers usually implement Divide and Conquer using recursion.
- Each recursive call represents a smaller subproblem.
- Recursion stops when the algorithm reaches the base case.
9. Time Complexity of Divide and Conquer
We express the time complexity of Divide and Conquer algorithms as:
T(n) = aT(n/b) + f(n)
Where:
- n = size of the problem
- a = number of subproblems
- n/b = size of each subproblem
- f(n) = time needed for dividing and combining
This formula forms the basis of the Master Theorem.
10. Real-World Applications of Divide and Conquer
- Book classification
- Mail sorting
- Sorting large datasets
- Searching operations
- Computer graphics and Artificial Intelligence
11. Conclusion
The Divide and Conquer algorithm helps you solve large problems by breaking them into smaller, manageable parts. When you apply this technique properly, you save both time and computational resources while keeping the solution simple and efficient.
- POP- Introduction to Programming Using ‘C’
- DS – Data structure Using C
- OOP – Object Oriented Programming
- Java Programming
- DBMS – Database Management System
- RDBMS – Relational Database Management System
- https://defineinfoloop.blogspot.com/?m=1